Canonical URLs – All You Need to Know

There is a lot to be said about even the basics of search engine optimization, and there is always more to learn. For instance, even if you optimize a page to within an inch of its life, it may still consist of much the same content as another page on your website. There are plenty of reasons why this may happen: web syndication, quotations, same or similar product descriptions, to name a few. Some of them are avoidable, some are fixable, and some you can do nothing about. In this article, we will be dealing with canonical URLs: a way to prevent duplicate content from hurting you by diluting your website’s authority.
But what does it mean for a page‘s URL to be canonical? Can you make it canonical, and can you decanonicalize it? What does it matter whether you do that or not? SEO seems more and more esoteric as it gets complex: there is a whole SEO argot, and SEO myths abound. It is easy for a novice user to get confused. In this article, we will be talking about canonical URLs: what they are and what they are good for.
Here‘s what this article is about:
In a nutshell, a canonical URL is the URL of a page a search engine prefers over other similar pages. Does that clear it up? No, not really. So let‘s take a step back.
Say you have two pages with very similar or identical content. They score equally for relevance and usefulness in the eyes of the search engines. This means that one is as good as the other, and therefore the attention of the search engines is split between the two equally, and they each rate half as much as they would if it were a single page.
However, Google, and possibly other search engines, selects one page, and one URL, as canonical, preferring it over others.
A canonical tag lets the search engine know which page is the master copy, as it were. This directs the attention of a search engine to it. You can indicate your preferred copy of a page by adding a canonical tag (a rel=”canonical” tag) to the page‘s head section: anywhere between the <head> tag and the </head> tag. It looks something like this:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.yourwebsite.com/yourpage/” />
Of course, you need to replace the placeholder text of the URL itself with a real URL. The canonical tag may refer to the page it is a part of, or it can be located in the head section of a non-canonical page, reinforcing the tag.
However, in determining which is the canonical page, Google (and, possibly, other search engines) uses not just the canonicalization tags, but also the website‘s sitemap, the page‘s relative age, and possibly other data. Exactly which signals are used is each search engine‘s business secret. This means that even if you set up a canonical page, a search engine might still choose another. That said, if you set up your canonical tags directly, the likelihood of a search engine ignoring your setup is very low.
This depends on what you are trying to achieve, as they do different things on a technical level.
A canonical tag is invisible to the user, as they will not ordinarily rifle through your page‘s code. They will simply be presented with your preferred copy of a page on a search engine results page, or SERP.
A 301 redirect is typically used in cases when there is a change to your content (when you delete a page, for instance), when a page‘s URL has been changed, or you have migrated your website to a different domain. A user sees the 301 redirect, and knows that they will be taken to a different page than the one they navigated to.
You can use 301 redirects to redirect all your users from a non-canonical page to its canonical version, but if you want to do it seamlessly, a canonical tag is the way to go.
In the article we linked to in the introduction, we went in-depth about duplicate content and how it affects your website‘s performance and SERP rankings, but we will reiterate the gist of it here, for your convenience.
Setting one URL as canonical over other pages which share the same content lets you pick the URL that is displayed to search engine users. This means that you can select a clean, clear, and simple URL instead of a confusing one. This way, you avoid technical issues such as percent-encoding from making your URLs appear suspicious to the user.
Furthermore, a page‘s authority is determined by how many links to it there are. This link capital determines your page‘s position in the SERPs. Canonicalization lets you direct all the link capital to the page indicated as canonical, meaning it is not diluted over same or very similar pages.
If you are operating a large website, with a huge number of pages, canonicalization means that search engine crawlers will ignore duplicate versions of your pages and concentrate on crawling new content to add them to their index. Canonicalization is crawl budget-efficient, in other words.
Finally, the same content may be published on different websites for a variety of reasons, not least of which being syndication resulting from collaboration with others. Such collaborations may include canonical URLs, to ensure that the original publisher gets the best ranking.
You can use code to specify canonical URLs, simply by copying the tag into a page‘s head section and configuring it. However, we do not recommend this if you are not a developer. Our coding-free alternative is Rank Math, our preferred SEO solution. If you are already using Rank Math in Advanced mode, scroll down to the relevant section of the tutorial. If not, read on.
After having installed and activated Rank Math, navigate to its dashboard by selecting Rank Math/Dashboard.
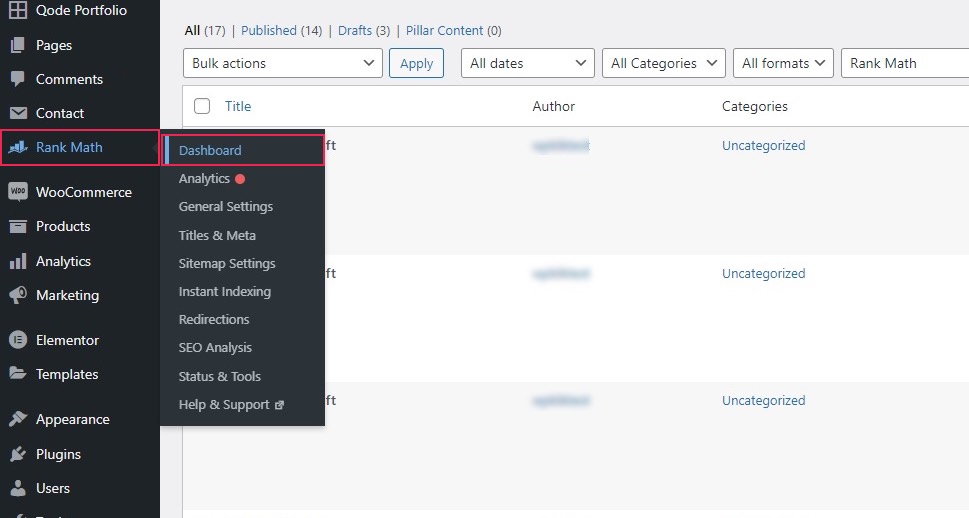
Once there, navigate to the Setup Wizard tab.
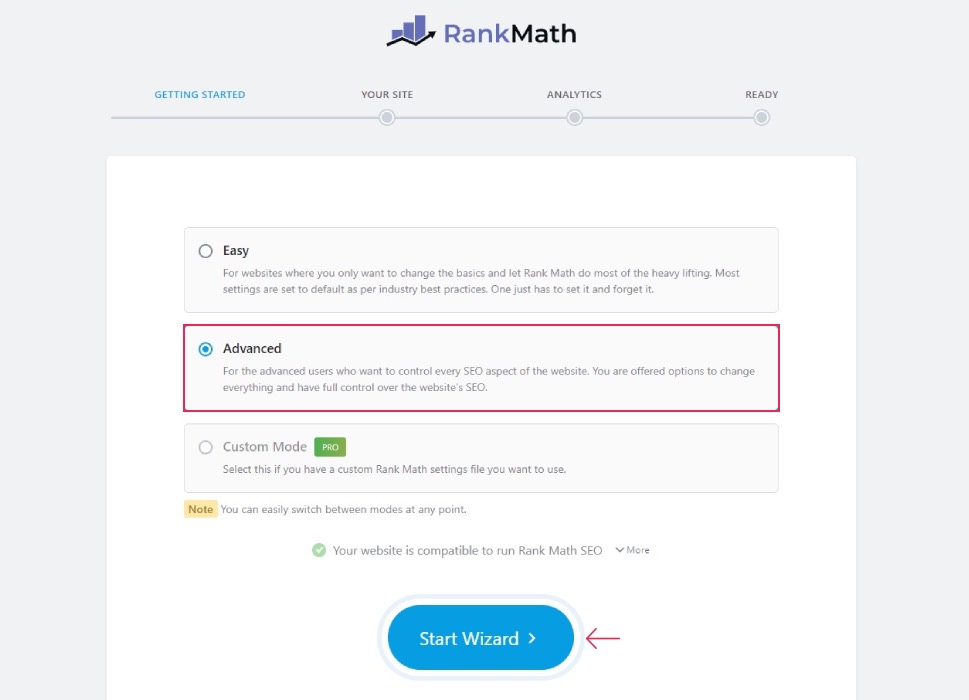
Select the Advanced mode and click the Start Wizard button.
From then on, follow the prompts on screen to configure the advanced mode for your website specifically.
Once you have the advanced mode activated, edit any page or post. Open Rank Math‘s meta box by clicking on the Rank Math icon, and select the Advanced tab.
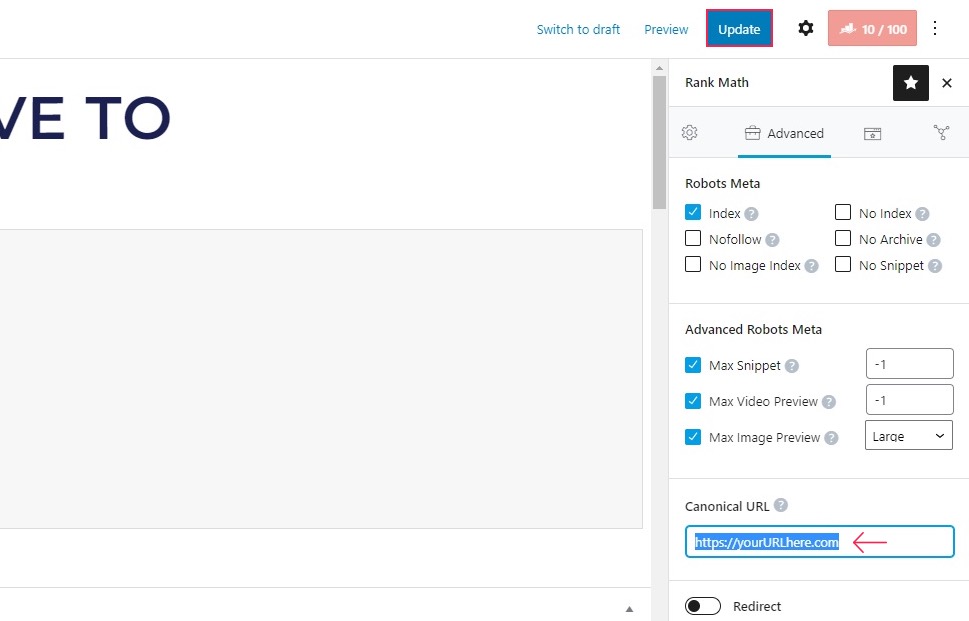
Finally, enter your URL in the Canonical URL field, and Update your post.
And your page or post‘s head section will be edited to contain the canonical tag.
In Conclusion
As you can see, canonicalization is a valuable tool in avoiding the issues stemming from duplicate content, whether on your own website or across the entire internet. Canonical URLs let you make the best possible use of your content‘s potential to gain you new visitors for your website, and you can make use of it with just a few clicks of the mouse and a little clever optimization.



