How to Fix Crawl Errors in Google Search Console

Like it or not, Google is the undisputed market leader in search engines. And if you know even the first thing about SEO, you know that Google is more than just a search engine. As more and more users find the content they want through search engines, Google provides more and more analytics and search optimization tools. Google Search Console, a tool that started its life as Google Webmaster Tools, is one of them. And in this article, we will be showing you how to use Google Search Console to get rid of crawl errors.
But what are crawl errors? How and why do they occur? How do they affect your website? These questions, and more, will be answered in this article. Here’s what we’d like to talk about:
As you may have gathered, crawl errors have to do with the basic mechanics of search engines. You can consult the linked article for a more in-depth view, but the gist of it is this: search engines do not search the internet. That would take up far too much time.
Instead, search engines use pieces of software variously called bots, robots, or crawlers to search websites and create an index, and search the index instead. The process of creating an index is called crawling. A bot crawls a page, adds it to the index, and adds all the links from a page to the list of links it has yet to crawl. Ideally, each and every link on a website will lead to a page.
Consequently, a crawl error is a situation in which a search engine attempts to crawl a web page but is unsuccessful. A bot attempts to reach a page on a site, but can’t.
For the purposes of Google’s functionalities, there are two kinds of crawl errors: site errors and URL errors.
If you have a site error, this means that your entire website cannot be crawled. This is known in SEO argot as a Very Bad Thing. If your website cannot be crawled, it means it cannot be indexed: your entire website, including all of its content, will be invisible to search engine users. It might still be reachable by typing the URL into the URL field of your browser, but when have you last done that?
If, conversely, your website has a URL error, it means that a specific page of your website is uncrawlable by bots. This is not a major issue (or at least not as major as a site error), and is usually your own fault – many URL errors stem from internal links.
You can see whether your website has any errors by navigating to your Google Search Console and selecting Coverage/Errors from the left-hand side menu.
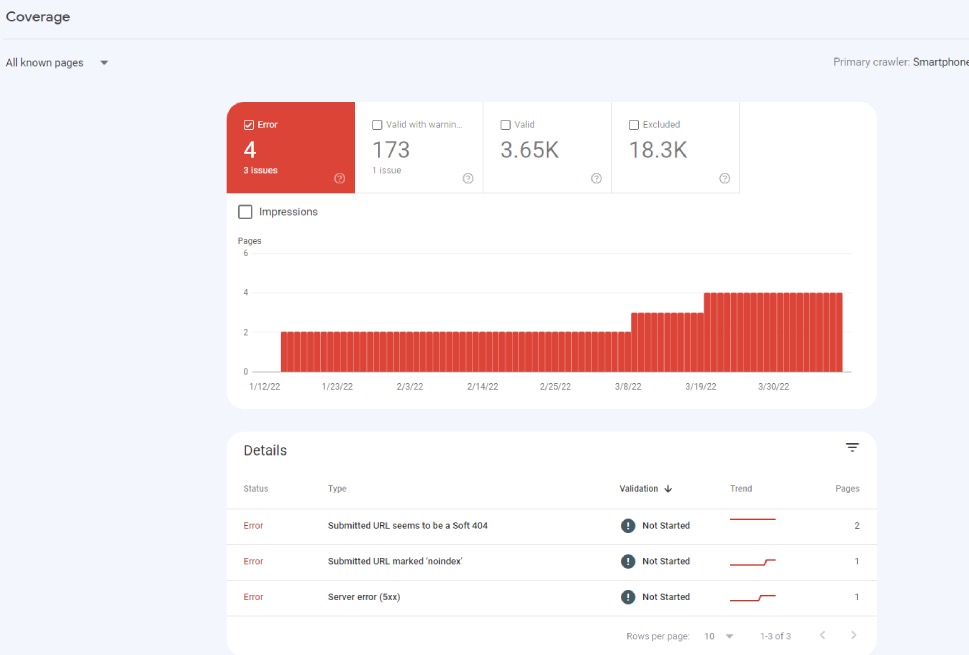
DNS Errors
DNS stands for Domain Name System, and it is what lets you navigate the internet without knowing each website’s IP address. If Google Search Console throws up this error, it means that your website can’t be reached. It can be temporary, in which case Google’s bots will attempt to crawl it later, but if the error persists, that means that Google has tried to reach it multiple times.
To test for this issue, use a tool such as downforeveryoneorjustme.com to test whether the website is down, and contact your domain provider immediately, as the issue is likely down to them. It may be a temporary issue, but it is unlikely that you alone have caused a DNS error and equally unlikely that you can fix it – unless you are your own domain provider.
Server Errors
A server error likely means a request timeout: your server is taking too long to respond. A crawler is attempting to visit and index your website, but the amount of time it takes your website to load is just too great to make it practical. Unlike a DNS error, a server error means that Google can reach your website, but the page takes too long to load. Alternatively, it may mean that your website is overwhelmed with requests, either through a large number of visitors, or a DDOS attack.
The Inspect URL tool is used to check how Google bots access a website. It is found on the right-hand side of the console.
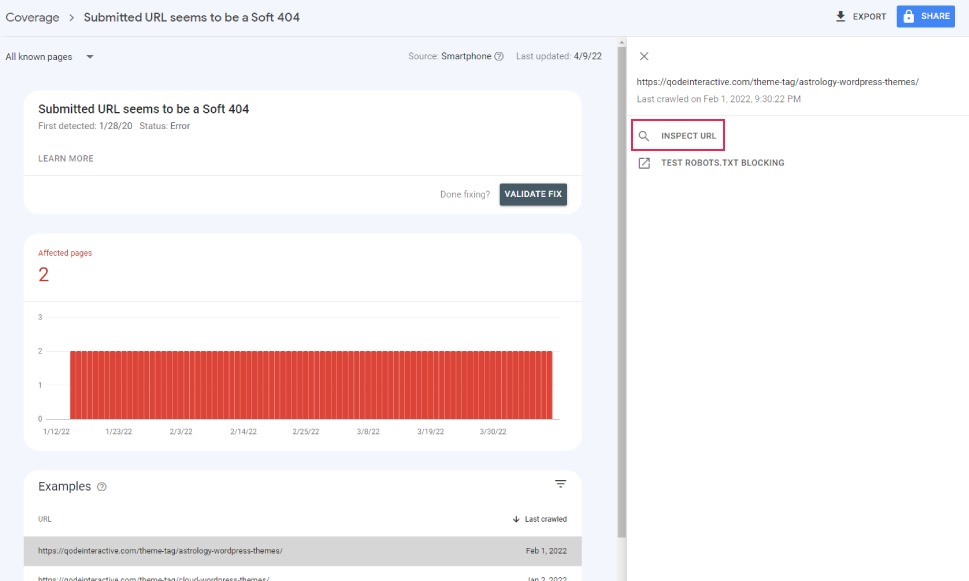
The Test Robots.txt Blocking tool is used to check the configuration of your robots.txt file which we’ll be covering in the following section.
If you have a server error, use the Inspect URL tool to find out exactly which of these issues has occurred:
-
timeout: the server took too long to respond to Google’s bots;
-
truncated header: the server closed the connection before Google could receive the full header;
-
connection reset: the connection was reset mid-response;
-
truncated response: the connection ended before Google could receive a full response;
-
connection refused: the server refused to connect with Google’s bots;
-
connect failed: the server was down or inaccessible;
-
connect timeout: the connection took too long to process;
-
no response: the connection was ended before any response was sent.
These can be temporary or they can stem from internal website issues. Explaining each of them in detail is well beyond the scope of this article, but we will refer you to the Google Search Console help once you have enough data to go on.
A robots failure means that Google’s bots cannot reach your website’s robots.txt file. We won’t go on about the robots.txt file – consult the linked article for more – but we will give you the gist: it is used to govern the behavior of search engine bots for various reasons. You don’t need it to have a fully functioning website, though. Google will just take it to mean that you want your entire website crawled and indexed.
Still, if you do have a robots.txt file, you need to make sure it is properly configured. Make sure the file does not contain this line:
disallow: /
This line makes your entire website unavailable to Google’s bots. If you want your website indexed, you need to erase this line. However, changing your website’s code is best left to professional developers. We suggest you seek help if you are not feeling confident. Remember, it is better not to have a robots.txt file at all than to have a poorly configured one.
404 Errors
A 404 error means that the content of a page cannot be found. Discussing the ways to fix a 404 error merits its own article, and you can consult the linked one for a detailed overview. Generally speaking, though, 404 errors do not affect your rankings with Google. If the pages which throw up the 404 are non-essential, this is not an urgent matter, but you should still fix them when you can find the time. If essential pages of your website are affected, you need to either fix it using the methods described in the linked article or set up a 301 redirect if appropriate.
Soft 404 Errors
Soft 404 Errors occur when a page looks like a 404 page but isn’t one. To whom does it look like a 404 page? To Google, in this case. Google is very good at guessing what a page’s content is. If an URL does not have a lot of “main content (meaning content other than links, headers, menus, and suchlike)”, it has an HTTP status of 200 (found) but not very much in what Google terms useful content.
If you want to avoid these errors, populate your soft 404 pages with actual content, or supply them with 301 redirects where applicable. Alternatively, if the page is permanently gone, allow 410 for the server header response.
Access Denied
In the case of a 404 error, Google’s bots can’t find a page. An access denied error means that they can’t. This typically means that it is blocked by your hosting provider, your robots.txt file, or you yourself required the user to be logged in to view the page.
Now, in the case of the former two, it may be just as you intended: if you don’t want a page to be crawled, your robots.txt file should contain the appropriate settings. Similarly, if you have set up a paywall or a similar login barrier, you don’t want your content to be available to any casual search engine user. However, if your hosting provider has blocked your content, you need to take it up with them.
Mobile-Specific Errors
These usually occur on non-responsive websites, and mostly entail faulty redirects to a separate mobile website. To fix them, check your redirects and your robots.txt as described in the robots failure section.
Google News Errors
If your website is on Google News, you might get crawl errors if your content is not formatted for Google News (faults in the headings structure, for instance), or they may happen when Google thinks your content is not a news article. You need to resolve them on a case-by-case basis.
Malware Errors
A malware error means that Google has found malicious software on a page. Again, protection from malware should be resolved on a case-by-case basis.
Server Errors and DNS Errors
Server errors and DNS errors may appear in the URL errors report on your Google Search Console report. This means that they are the same as site-wide errors, except for the fact that they affect specific URLs. You need to deal with them the same way you would deal with site-wide errors of the same kind.
Marking URL Errors As Fixed
Do it. Do it.
If you suspect the issue is temporary, or that it stems from a robots.txt file or paywall which was configured just the way you want it, you can mark all such URL errors as fixed. It won’t affect the performance of your website.
In Conclusion
As you can see, the Google Search Console is an important diagnostic tool. To keep your website functional and your visitors happy, check for errors regularly. A lot of the troubleshooting work is a slog, but some of the important stuff is also urgent. With Google Search Console and this handy guide, you’ll know which is which.



