WordPress User Roles: What Are They and How to Use Them

Launching a WordPress website can seem a bit challenging, especially if you’re a beginner. But truth be told, it’s not so complicated. Au contraire, the platform as a whole is quite intuitive and easy to navigate. It’s just that getting the hang of things can take some time, that’s all. To make the entire process of website building and, later, maintaining, a bit easier on yourself, it might be a good idea to distribute the workload. And this is where WordPress user roles come into play. So, let’s take a look at what WordPress user roles are exactly and how you can use them to your advantage.
What are WordPress user roles?
The WordPress role management system enables you to have multiple users in charge of specific areas of your website. Each role ensures different capabilities as well as levels of access. What’s even better is that you, as the website owner, get to determine how much power other users have and which actions they can take. This is incredibly important, as you don’t want to risk someone mismanaging your website.
WordPress comes with five pre-determined roles: Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor, and Subscriber. Each role has a set of default capabilities, and you can also remove or assign additional capabilities to every role.
Let’s get down to business, shall we? It’s time we learn more about all of these WordPress user roles and see how to make the most of them.
1. Administrator
The moment you create a WordPress website, you instantly become its Administrator. This role is the most powerful one of the aforementioned five. As an Administrator, you have complete control over your content. You can also edit core files, make changes in the theme editor, manage plugins, create and modify other user accounts, etc… Basically, you can do just about anything.
There should be only one WordPress website Administrator. And ideally, it should be precisely the website owner. However, if you plan on letting someone else serve as your site admin, choose someone you can place complete trust in. After all, you’ll be giving complete power over your website to that person, so make sure it’s someone reliable.
2. Editor
Editors are in charge of creating, editing, publishing, and deleting the content of your website, for both post and pages. They can also moderate the comments section, as well as manage categories and links. Editors take care of not only the content they create on their own, but also what other authors submit.
Unlike administrators, editors can’t manage plugins and themes, nor can they create new user roles. Their dashboard comes with fewer options and they can’t even access the general WordPress settings.
3. Author
This user roles comes with even less authority. An Author can write, modify, publish, and delete his or her own content, but can’t see what other users have created. They can upload files in the media library, but they don’t have the authorization to remove them. As regards to comments, they can view them all, but can reply to and edit only the comments on their own posts, not those on other authors’ posts.
4. Contributor
The role of a Contributor comes with significant limitations. It’s ideal for guest bloggers and those who don’t post on the regular. Contributors can write, edit, and delete their own posts, but can’t publish anything. Once they finish writing, an Administrator or an Editor needs to review their posts, before clicking Publish. Contributors can’t access the media library, so if they wish to use it, an Editor or an Admin must assist them. They can read comments, but don’t have the authorization to manage them.
5. Subscriber
Every new user becomes a Subscriber by default. Subscribers have only a handful of options in WordPress. They can read the content, write and post comments, manage their profiles, and that’s pretty much it. This is the most basic user role, but it comes in handy if users need to login to your website in order to read your posts and leave comments.
Super Admin – WordPress Multisite
As you probably already know, WordPress comes with a multisite feature, which enables you to set up a network of sites on a single WordPress installation. A Super Admin is someone who’s in charge of the entire network. This user role controls all the websites in the network as well as every single site feature. Super Admins can add or remove other websites from the network, and also change the capabilities of a regular Administrator and of other user roles.
User Roles in WooCommerce
When you add the WooCommerce plugin to your website, two additional user roles become available – Shop Manager and Customer. Also, as an Administrator, you gain the capability to manage all WooCommerce settings and to view WooCommerce reports.
Shop Manager
A Shop Manager is someone who’s in charge of your online store. They take care of all the settings regarding WooCommerce, and can also edit or create new products. Shop Managers can view reports, orders and order history, as well as manage their own account.
Customer
If a new user registers on your website using the signup or the checkout option, they are immediately assigned the Customer user role. Customers have read access only, similar to that of Subscribers. Furthermore, they can view their orders and order history, as well as edit their own accounts.
Creating Custom User Roles
If the existing WordPress user roles don’t suit your needs, you can either modify them by adding additional capabilities or simply create custom user roles. There are plugins that can help you do this, and the one that we’d like to recommend is the Capability Manager Enhanced plugin.
Upon downloading and activating the plugin, from the menu on the left select Users > Capabilities.
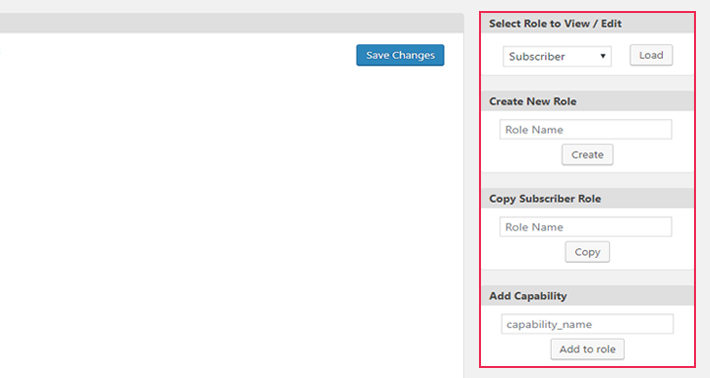
Now, this is where you can play around a bit and choose which capabilities each WordPress user role will have.
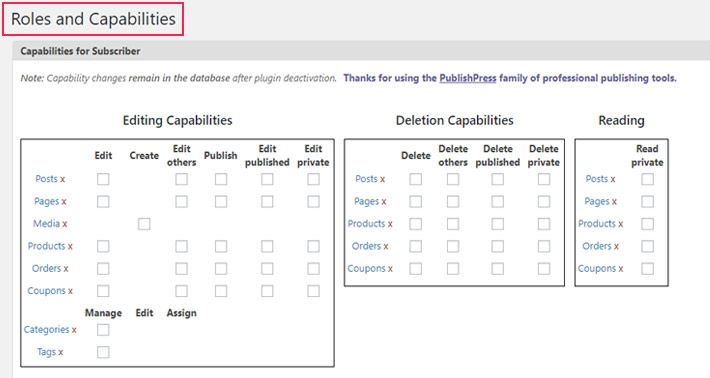
To assign a new role to a user or to create an entirely new user role, check out the options on the right side of the screen. This is where you can copy the predefined roles, and assign custom capabilities to each role.
How to Assign WordPress User Roles
To assign a certain role to a user, you must be either Administrator, or, in the case of a WordPress multisite, Super Admin. The action of assigning roles is quite simple and you can complete it in just a few steps:
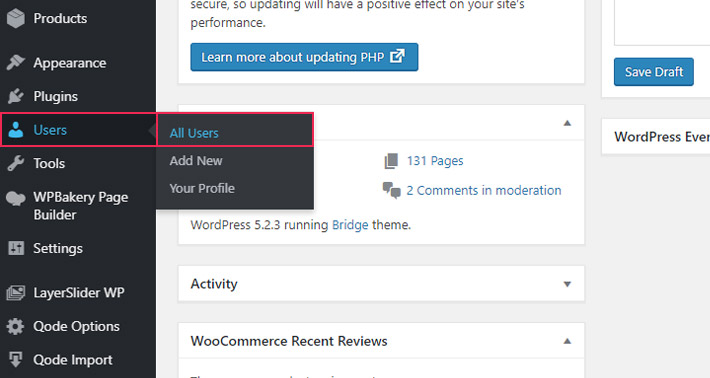
1. Users > All Users
For starters, go to Users on your admin dashboard and select the All Users option.
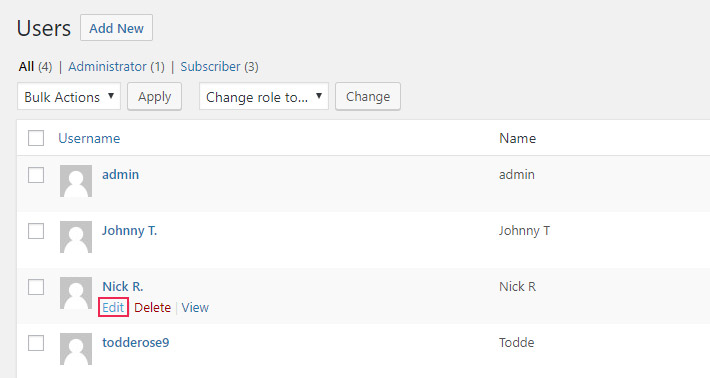
2. Edit
This is where you can see the list of all the website users. To modify a user profile, click Edit, beneath the username.
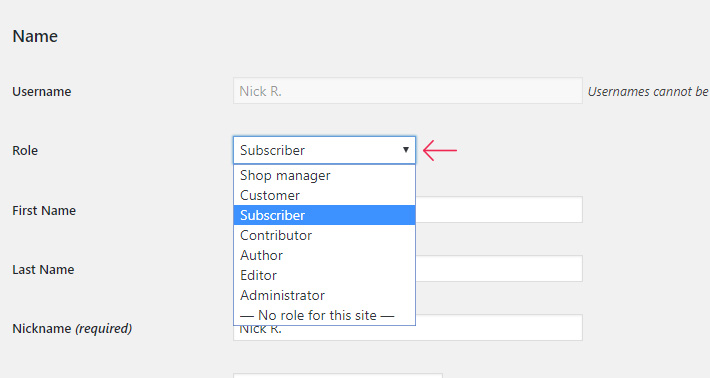
3. Assign a Role
Scroll down the long list of options until you find the Role section. From a number of options, choose the role you wish to assign to that specific user.
4. Disable the Visual Editor When Editing
Aside from assigning user roles, under Personal Options (on the same page), you have the possibility of removing the Visual Editor for any user. To do this, just check the Disable the visual editor when editing box.
5. Save
Once you’re done with editing a user role, click the Update Profile button to save your changes.
Conclusion
If a team of people is working on your WordPress website, it’s crucial to assign different user roles to each member. You want things to run smoothly and for your content to be secure. This is why everyone needs to have strictly defined levels of access, so they can’t make unauthorized changes. It’s for the best to work with only one Administrator or Super Admin, and a few trusted Editors. You can assign the Author role to the regular content creators, and all new writers should start off as Contributors. If you’re not happy with the default settings WordPress comes with, don’t forget that you can customize the user roles via a plugin.